Pneumococcus - on safety (MSDS) NAME: Streptococcus pneumonia SYNONYM OR Links: pneumococcus,
dyplokokk, Pneumococcal pneumonia
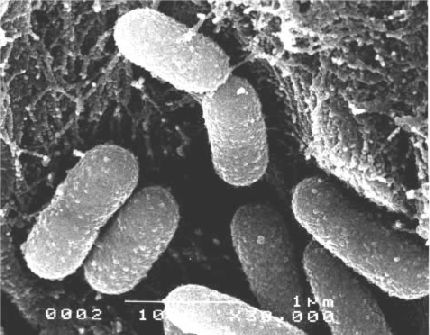
CHARACTERISTICS: Gram-positive diplococci,
alpha-hemolysis on blood agar, no specific antigen group
optionally anaerobic, lancet form or in chains, more than 90 serotypes
pathogens: sudden onset of chills sotryasayuschyy,
pleural pain, dyspnea, cough productive of sputum and rusty
leukocytosis, clinical signs include pneumonia, bacteremia,
otitis media, meningitis, sinusitis, peritonitis and arthritis;
Begin may be less dramatic in the elderly requiring x-rays for diagnosis;
in children vomiting and convulsions may be the initial manifestations;
important causes of death in infants and the elderly, 5-10% mortality
with antibiotic therapy, and 20-40% among patients with
underlying disease, neurological complications and / or training
disabilities may occur in patients with meningitis

EPIDEMIOLOGY: Continuing endemic
especially in childhood, old age and alcoholics more often
industrial cities and low socio-economic groups found in the >> << climate and season, the highest incidence in winter and spring in temperate zones
usually sporadic in North America, but can occur in epidemic
in enclosed public
hosts: infectious dose: mode of transmission: by airborne droplets, by direct
oral contact, indirectly, via contaminated fresh articles
with respiratory discharges, human-to-human transmission
organisms are common, but illness among casual contacts and attendants
rarely incubation period: communicability: Infectious classified as
mouth and nose no longer contain virulent pneumococci in
considerable amount penicillin provides patient noninfectious
within 24-48 hours, many people are carriers, the risk of infection
after contact with a carrier or infected person low, except
institution
Reservoir: zoonoses: sensitivity vectors drug: drug-resistant high level resistance to penicillin
; resistance to other therapeutic agents such as TMP / SMX,
erythromycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, ceftriaxone and cefotaxime
susceptibility to disinfectants:
susceptible to many disinfectants - 1% solution of sodium hypochlorite, 70% ethanol, 2%
hlutaraldehyd, formaldehyde, iodine << Physical >> inactivation : survival BEYOND Head: Observations: FIRST AID / treatment: penicillin G, enter
parenterally (erythromycin for those hypersensitive to penicillin
) >> << Immunization: Prevention: acquisition of infection by laboratory methods: 78 recorded
cases streptococci. 4 deaths in 1976, and the fifth
The most common infections in the lab
sources / samples: sputum, blood, respiratory secretions
, throat swabs
PRIMARY danger: Specific hazards: MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS: 2-level biosafety containment practices
equipment and facilities for all >> << activities involving known or potentially infected clinical materials and cultures
; animal 2 First level biosafety facilities for research using
infected animals Protective Clothing: Other precautions: spill: Allow aerosols to decide to wear
protective clothing, gently cover spill absorbent> ;> << a paper towel and apply 1% sodium cheap strattera hypochlorite solution from the perimeter and working
in the center, to provide sufficient contact time (30 min) to clear
WASTE : disinfection before disposal;
steam sterilization, chemical disinfection, incineration
STORAGE: Date prepared: May 2001
Prepared by: Office of Laboratory Security,
PHAC Although the information, opinions and recommendations contained
in this MSDS, they compiled from sources
, believed that strong, we are not responsible for the accuracy and adequacy
reliability or for any loss or damage >> < <the use of this information. Recently discovered dangers
often, and this information can not be completely up to date with
. Health Canada, 2001. << >>